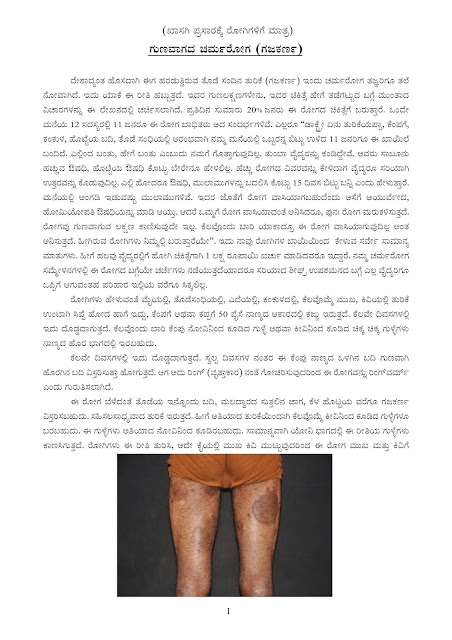
Vitamin deficiency, stress, genetic factors & food hypersensitivity cause mouth ulcers
Mouth Ulcers
Mouth ulcers, known as
aphthous ulcers, are one of the common issues faced by people and are an
annoying and painful condition. According to Senior Dermatologist Dr K.S.
Prasanna, though the cause of mouth ulcers is not known, generally they are
triggered or influenced by trauma, iron, folate or vitamin B12 deficiency,
hormonal fluctuations, psychological stress, infections, food hypersensitivity,
or genetic factors.
Generally, ulcers are
of three types: minor (small ulcer), major (large), and herpetiform (grouped).
Minor ulcers are shallow and painful ulcers that are usually less than 5mm and
seen mostly on lips and cheeks. About 80 percent of ulcers are of this type.
The most common sites of involvement of the oral mucosa are inner lips, cheeks,
and lateral margin of tongue. The ulcers last for 4-14 days with a rate of
recurrence ranging from 1-4 months in an irregular pattern. Major ulcers are
more than 10mm, last for one month, and are seen on lips, cheeks, tongue,
pharynx, palate, and gums. They are deeper, persist for up to 6 weeks, and may
heal with scarring. Major ulcers are associated with considerable pain and are
sometimes accompanied by fever and malaise. Around 10 percent of patients have
this form of ulcer. These ulcers can stay for months.
Herpetiform ulcers are
recurrent tiny ulcers, and few are
clustered. They can affect any part of the mouth, including gums. They are
1-2mm in size but can join together and last for 7-10 days. This type of ulcer
is seen on lips, cheeks, tongue, pharynx, and floor of mouth.
"Always consult a
medical expert if the ulcers persist. A correct diagnosis is necessary to rule
out any major diseases associated with apparently benign mouth ulcers..
Avoiding toothpaste with sodium lauryl sulfate, smoking, and diet containing
benzoates, cinnamaldehyde, chocolate, and sorbic acid is also
recommended," Dr. Prasanna said, adding that the primary goal of therapy
is promotion of healing, management of pain and nutrition, and prevention of
recurrence. "non-herpetic oral ulcers are not contagious. Early and
effective treatment of these ulcers minimizes the discomfort and pain. However,
even without treatment, benign mouth ulcers usually go away within two weeks.
If they don't go away after two weeks, then consult a doctor," she added.


Comments